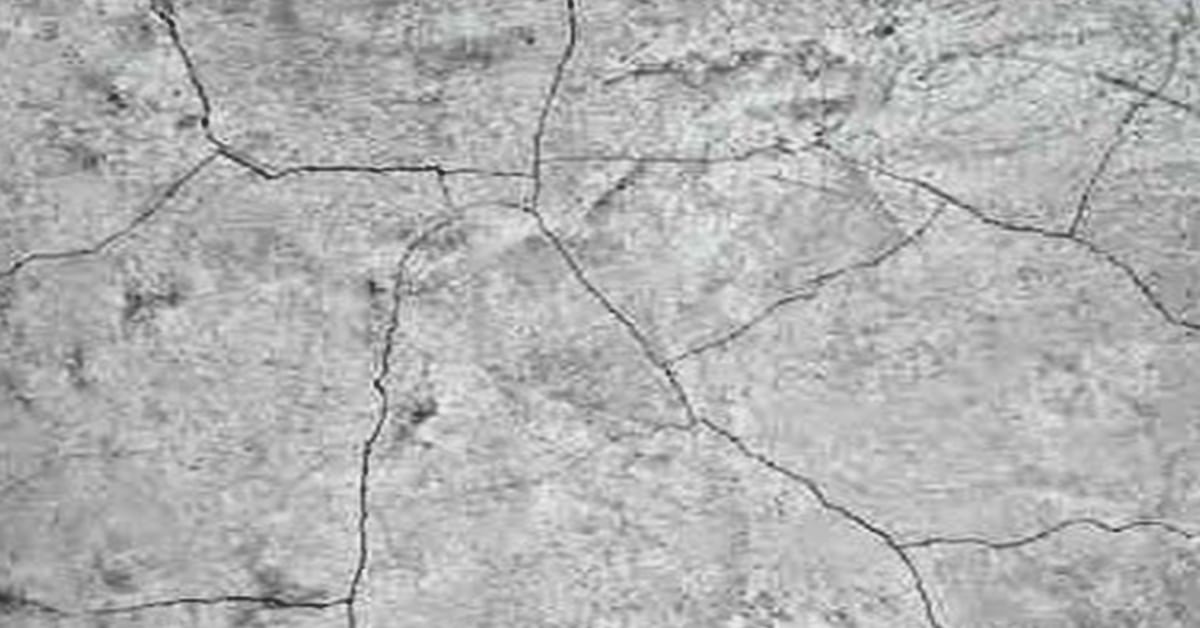
Plastic shrinkage cracks generally occur during first 7 seven hours after casting, and in most cases the cracks are only noticeable the next day. Fresh concrete has very little strength when it is placed in the mould. At this time, the mixing water in the concrete is free to move and also very to appear in the surface due to its low density. This scenario is more critical during compaction, where the heavier material will settle down forcing the lighter material to float up. This phenomenon is also known as bleeding.
What Causes Plastic Shrinkage in Concrete?
The water that appears at the surface has remarkably high tendency to disappear mainly due to evaporation, and this results in contraction in the concrete which known as plastic shrinkage.
The shrinkage action is mainly caused by the surface tension force. To what extend your concrete will shrink is depends on the amount of water lost, and this is directly influenced by the temperature, relative humidity, and the wind.
As rule of thumb, if the water lost due to evaporation is greater than the water appears due to bleeding, then there is a net reduction in the volume of the concrete. In such situation, the surface will tend to shrink, but restrained by the layers below it.
The restraint happens because the underlying layers does not go through the water loss; therefore, eliminating the need to shrink. As a result of the restraint, the concrete surface will experience the tensile stress, which is obviously no good for concrete. Till now the concrete is still in plastic state, which means has very little strength. Thus, this would result in crack formation on the concrete surface.
Typically, the plastic shrinkage cracks can be observed visually; because the cracks tend to be up to 3mm wide and vary in length depending on your surface area. The depth of the crack is normally around 20 to 50mm, and there are cases where the cracks penetrate through the whole depth of the element.
Another obvious characteristic of this type of cracks is that it normally does not extend to the edge of the slab, mainly because at this area the shrink without restrain is possible.
How to control plastic shrinkage?
As we all know prevention is better than cure; therefore, let us look at ways to prevent plastic shrinkage cracks. The key control factor in plastic shrinkage is the rate of evaporation, and this is directly related to relative humidity and wind speed. A hot windy day will give a very high rate of evaporation, and most of the time this is beyond our control. So, one of the easiest way to save the concrete from high evaporation is by providing proper and adequate curing. Apart from proper curing, listed below some of the other ways you can employ to minimize the plastic shrinkage effect.
- Make sure the surface of the concrete is dampened frequently.
- During hot weather concreting; use ice cubes or chilled water for mixing concrete.
- Protect the concreting area from direct wind. This would reduce the velocity of the wind passing over the surface of the newly placed concrete.
- Keep the temperature of concrete low by substituting the cement with alternative pozzalanic by-products. GGBFS has been found to be an excellent alternative in keeping the concrete temperature low and improving concrete durability
- Cover the surface of newly placed concrete with plastic sheet or gunny sack to avoid any moisture loss and retain the moisture in concrete.
- You also can use synthetic fibers (glass fibers, Steel fibers, etc) in the concrete. Apart from many other benefits of adding fiber in concrete; the fibers in concrete also has been found to help in crack prevention.
- The mist fogging or mist fan also can be used to bring down the temperature of the concreted area.
- Plastic shrinkage cracks happens during the period where the concrete stays in plastic state. Therefore, to minimize the potential for plastic shrinkage, the setting time should be accelerated. Some of the methods listed above could potentially prolong the setting time. The use of any kind set accelerator could reduce the setting time of concrete.
Correcting the Plastic Shrinkage
Though this type of cracks usually does not cause any structural integrity problem; it is still very important to take necessary action to close it back to avoid reinforcement corrosion. Since these cracks happen while the concrete still in plastic state, it is easier to seal the crack back.
The easiest method is by spreading some cement powder on the cracked concrete surface and brushes it into the cracks. Once the cracks are filled with cement, use a dampened cloth to level it. This action is possible if the concrete is still in plastic state, and shall be done as soon as possible, so that the old concrete and new cement can cure homogeneously.
If the concrete has passed the plastic state, then you could use low-viscosity resin to inject into the crack. This is also a very successful method, but more costly.
Additional Reading & Reference Material
Properties of Concrete – by A.M. Neville.
Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, And Materials – by J.M. Paulo Monteiro P. Kumar Mehta
ASTM C1579 – 13 Standard Test Method for Evaluating Plastic Shrinkage Cracking of Restrained Fiber Reinforced Concrete (Using a Steel Form Insert)
ACI 224.1 R 07 – Causes, Evaluation, and Repair of Cracks in Concrete Structures